Reporting reimbursements of expenses to the Incomes Register
Reimbursement of expenses means that the employer or another payer reimburses the employee for expenses incurred during the performance of work.
An employee may incur expenses from, for example, business travel and the acquisition of tools, materials, supplies or protective clothing. The employer may also pay a reimbursement to the employee using their own tools during work.
Taxable reimbursements of travel expenses paid by the employer must also be reported to the Incomes Register. Such travels include leisure-time trips reimbursed by the employer, trips between home and the workplace and hotel stays, and they must be reported, because these reimbursements do not meet the general requirements for being tax-exempt and are deemed equivalent to wages.
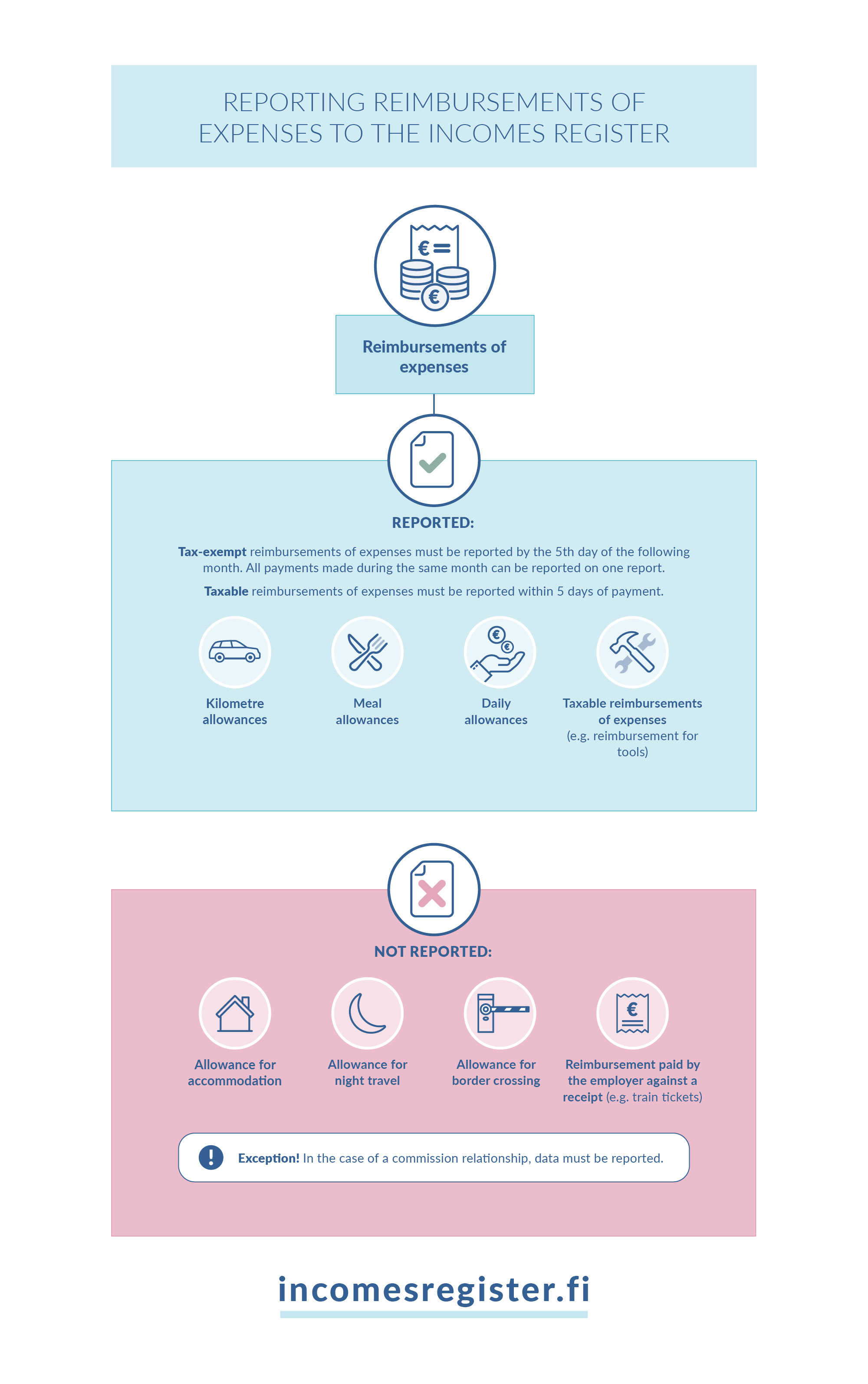
Which reimbursements of expenses must be reported to the Incomes Register?
Reimbursements of expenses are reported on an earnings payment report using their own income types, regardless of whether the cash wages were reported as a total amount or as itemised amounts. The exception are reimbursements of expenses paid in connection with a non-wage compensation for work; these are discussed later in these instructions.
Tax-exempt and taxable reimbursements of expenses are reported to the Incomes Register. Some taxable reimbursements of expenses can be paid without withholding tax. Reimbursements of expenses can be paid by, for example, employers, associations and households.
Tax-exempt reimbursements of expenses
Report tax-exempt reimbursements of expenses paid in addition to wages in accordance with the Tax Administration's decision (so-called decision on expenses).
- Report them using income types Meal allowance (303), Kilometre allowance (tax-exempt) (311) and Daily allowance (331).
- Report the reimbursements of travel expenses between the residence and special place of work paid in the construction sector using income type Kilometre allowance (tax-exempt) (311).
Tax-exempt reimbursements of expenses (kilometre allowances, daily allowances and meal allowances) can be reported by the fifth day of the month following the month of payment. The payments can be reported using a single report once a month, even if reimbursements of expenses have been paid on several days during the same month. In such a case, the payment date entered on the report must be the latest payment date of reimbursements of expenses.
Exception: Tax-exempt reimbursements of expenses paid by non-profit organisations or public sector payers involve special limitations:
- The maximum amount of tax-exempt kilometre allowances that can be paid to one income earner is EUR 3,000 per calendar year. Report the kilometre allowances using income type Kilometre allowance paid by non-profit organisation (357). Report the part exceeding the tax-exempt part using income type Non-wage compensation for work (336).
- With respect to the reimbursement of travel expenses, tax-exempt daily allowances may be paid to one income earner for a maximum of 20 days per calendar year. Report the reimbursements of travel expenses using income type Daily allowance paid by non-profit organisation (358). Report the taxable amount exceeding the tax-exempt daily allowances using income type Non-wage compensation for work (336).
A shareholder in a limited liability company or a shareholder in a partnership may work for the company without withdrawing wages. Despite this, they may be paid tax-exempt reimbursements of travel expenses for business travel on behalf of the company. In such a case, the requirements for the reimbursements of expenses being tax-exempt must also be met. Report the reimbursements of expenses paid using income types Meal allowance (303), Kilometre allowance (tax-exempt) (311) and Daily allowance (331).
Taxable reimbursements of expenses
Taxable reimbursements of expenses are:
- expenses directly incurred from work that the employer has not included in the amount of wages when withholding taxes
- reimbursements of expenses that are wages and subject to withholding.
Taxable reimbursements of expenses must be reported to the Incomes Register within five days of the payment date, even if no cash wages are paid at the same time.
Expenses directly incurred from work that are not included in the amount of wages
Report taxable reimbursements of expenses directly incurred from work using one of the following income types:
- Report using income type Taxable reimbursement of expenses (353) if the employer has paid the expenses separately (in addition to the wages) and has not withheld taxes from them.
- Report using income type Deduction before withholding (419) if the employer has deducted the share of the expenses from the gross wages before the withholding calculation.
Exception: Municipalities can also pay taxable reimbursements of expenses that are reported using the following income types:
- Reimbursement of private caretaker's expenses (327)
- Reimbursement of family day care provider's expenses (329)
- Reimbursement of costs, paid to conciliator (335). In addition to municipalities, reimbursements of costs paid to a conciliator can be paid by associations (so-called mediation offices).
Expense items subject to withholding and deemed to be wages
An employer can pay reimbursements of expenses that are deemed to be the employee's wages. The expenses are then taxable and the employer must withhold tax from them.
If reimbursements of travel expenses are paid for trips on which the employee is not entitled to tax-exempt reimbursements, the travel expenses are deemed to be wages. These include reimbursements the employer pays for trips between the employee's home and actual workplace. Report reimbursements of travel expenses deemed to be wages using income type Other compensation (216). If the travel is reimbursed according to the use of the employee's own car, you can use income type Kilometre allowance (taxable) (209).
If the employer pays reimbursements of travel expenses in accordance with the Tax Administration's decision, but the amount of the reimbursement exceeds the tax-exempt amount specified in the decision, the excess part is considered the employee's wages.
Example: The maximum amount of tax-exempt domestic full daily allowance that can be paid is EUR 53 per day. If an employee goes on a business trip and is paid a daily allowance of EUR 53 per day, the allowance is tax-exempt. If, however, the employee is paid a daily allowance of EUR 56 per day, the part exceeding EUR 53, or EUR 3, is a taxable reimbursement deemed equivalent to wages.
The deciding factor in reporting daily allowances and kilometre allowances is whether the allowance is paid in accordance with a collective agreement or not.
Daily allowance is paid in accordance with a collective agreement: Report using income type Other compensation (216). Also use the Type of insurance information section to report that the income is not subject to earnings-related pension, unemployment or accident and occupational disease insurance contributions. However, the income is subject to a health insurance contribution.
Daily allowance is not paid in accordance with a collective agreement: Report using income type Other compensation (216).
Kilometre allowances are paid in accordance with a collective agreement: Report using income type Kilometre allowance (taxable) (209). If the allowance paid matches the maximum amount specified in the Tax Administration's decision, also use the Type of insurance information section to report that the income is not subject to earnings-related pension, unemployment or accident and occupational disease insurance contributions. However, the income is subject to a health insurance contribution.
Kilometre allowances are not paid in accordance with a collective agreement: Report using income type Kilometre allowance (taxable) (209).
If the taxable kilometre allowances are paid to a commissioned recipient who is not registered in the prepayment register; however, they are reported using income type Non-wage compensation for work (336).
Meal allowance: Report using income type Other compensation (216).
Which reimbursements of expenses are not reported to the Incomes Register?
Tax-exempt reimbursements of business-related travel expenses are not reported to the Incomes Register if the employer pays the reimbursement to an employee in an employment relationship against a document provided by the transport operator (such as a train ticket). Accommodation allowances are not reported to the Incomes Register. Neither are night travel allowances or border-crossing allowances reported to the Incomes Register if they are paid in accordance with the maximum amounts specified in the Tax Administration's decision. If the employer has paid a travel advance to the employee before the beginning of the business trip, and the employee has used the full amount of the travel advance to cover the travel expenses, the travel advance is not reported to the Incomes Register. If, however, some of the travel advance remains unused, and other tax-exempt travel expenses incurred by the employee are offset from it, the amount of the offset is reported to the Incomes Register. The part deemed to be expenses reimbursed to the employee is reported as a daily allowance, kilometre allowance or reimbursement of expenses.
The following reimbursements of expenses are not reported to the Incomes Register:
- reimbursement paid to an employee in an employment relationship based on a document provided by the transport operator (such as a train ticket);
- tools and work materials acquired by the employee on behalf of the employer if the employer has reimbursed the employee for the acquisitions against a document;
- accommodation allowance;
- night travel allowance, if it is paid in accordance with the maximum amount specified in the Tax Administration's decision. The excess part is reported using income type Other compensation (216);
- border-crossing allowance, if it is paid in accordance with the maximum amount specified in the Tax Administration's decision. The excess part is reported using income type Other compensation (216); and
- travel advance, if no travel advance remains unused.
Did you purchase a service from a business and paid against an invoice?
Non-wage compensation for work is paid based on an assignment to an entrepreneur or a business against an invoice. Reimbursements of expenses paid to entrepreneurs or businesses are always fully taxable.
Non-wage compensations and reimbursements of expenses paid to entrepreneurs or businesses are reported to the Incomes Register only when the income earner is not registered in the prepayment register. If you pay a non-wage compensation for work and reimbursements of expenses to an entrepreneur or a business not registered in the prepayment register, total the amount of the non-wage compensation for work and the reimbursements of expenses. Report the total amount, VAT excluded, on an earnings payment report using income type Non-wage compensation for work (336). Read more about the situations in which you need to report non-wage compensations for work to the Incomes Register.
If a non-wage compensation for work is not reported to the Incomes Register, neither are the related reimbursements of expenses reported.
The exception is a situation where the payer is covered by the public sector pensions act (julkisten alojen eläkelaki 81/2016). Read more about how a JuEL payer reports non-wage compensation for work it has paid to the Incomes Register.
