Reporting non-wage compensations for work
A non-wage compensation for work is compensation paid for work that is not pay. The person that performs the work is not employed by the party that pays for the work; the payer commissions the work from its performer, i.e. purchases a service.
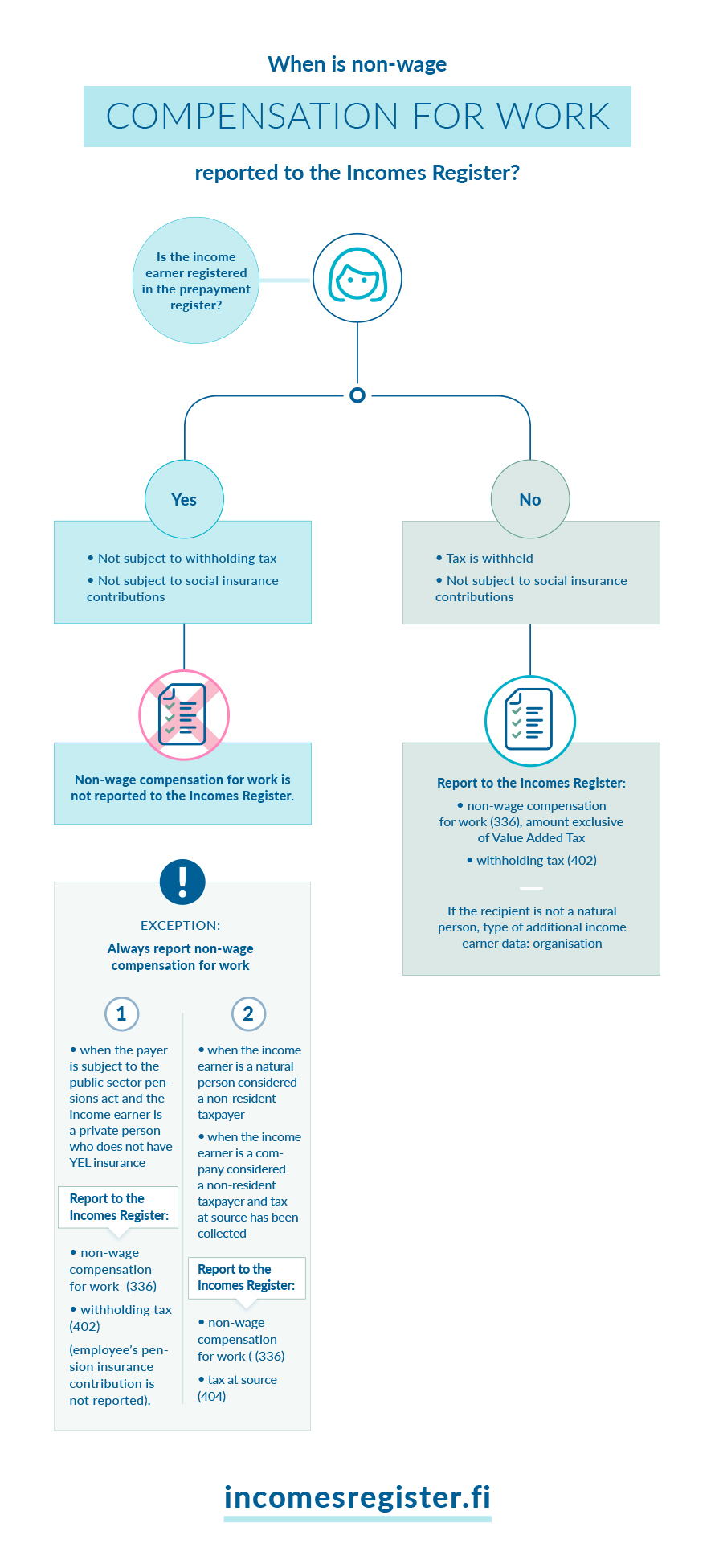
When you buy a service from a company or individual, visit the Business Information System (BIS) to see whether the service provider is in the prepayment register.
Non-wage compensations for work do not usually need to be reported to the Incomes Register if the service provider is registered in the prepayment register
You only need to pay the invoice for the work done. You do not need to report the payment to the Incomes Register.
However, non-wage compensations for work must be reported in the following situations, even if the service provider is registered in the prepayment register:
- The non-wage compensation for work is paid to a non-resident taxpayer
- The non-wage compensation for work is paid to a company considered a non-resident taxpayer and you have collected or should have collected tax at source from the non-wage compensation for work.
- You are a payer subject to the public sector pensions act and the non-wage compensation for work is paid to a person who is not insured under the self-employed persons’ pensions act
In these situations, report the non-wage compensation for work according to the instructions below.
Report the non-wage compensation for work to the Incomes Register, if the service provider is not registered in the prepayment register
Report the non-wage compensation for work you have paid to the Incomes Register by submitting an earnings payment report within 5 days of the payment date. As there is no lower limit for the amount you have paid, you also need to report any small amounts.
Read more on how to report this information to the Incomes Register
Enter the following information on the report:
- The payment date – the date on which the payment is in the recipient’s account.
- The pay period – report the first working day as the start date and the last working day as the end date.
- The payer’s name and personal identity code or business ID.
- The name and identifier of the recipient of non-wage compensation for work; for example, a personal identity code or business ID. Also include the information that the income earner is a non-resident taxpayer, if applicable.
- Enter the additional income earner information as follows if the receiver is one of the following:
- 'Organisation' if the payment recipient is a general partnership, limited partnership, limited liability company, cooperative, association, foundation or some other legal person governed by civil law.
- ‘Athlete’, if the receiver is an athlete.
- ‘Performing artist’, if the receiver is a stage or film actor, a radio or television performer, or a musician.
- The amount of the non-wage compensation for work with the income type Non-wage compensation for work (336).
- Include the share of the work without value added tax and any travel expenses itemised on an invoice in the amount.
- Do not include other expenses such as material expenses itemised on an invoice to the amount of the non-wage compensation for work.
- Enter the amount withheld using the income type Withholding tax (402) if you have withheld taxes from the non-wage compensation for work. Correspondingly, enter the amount of tax at source using the income type Tax at source (404), if you collected tax at source.
Select the correct income type – separate incomes types for some non-wage compensations for work
The following are examples of payments that are reported with the income type Non-wage compensation for work (336)
- compensation for work carried out based on a commission, e.g. compensation for a service you have bought or work you have commissioned
- trustee's fee
- athlete's fee
- performing artist's fee
- allowance to witness
- finder’s fees
- payments or reimbursement of expenses made to a support person
- reimbursements of travel expenses paid by an entity promoting the public good, for the part that they exceed the tax-exempt amount
- voluntary perquisite (tip).
The following are examples of payments that are reported with their own income type:
- Private caretaker’s fee (328), also use this income type to report payments made for support family activities
- Reimbursement of private caretaker's expenses (327)
- Private day care allowance (non-wage) (356)
- Kinship carer's fee (319)
- Reimbursement of costs, paid to conciliator (335)
- Dividends/profit surplus based on work effort (non-wage) (340).
See more examples and read more about non-wage compensation for work: Reporting data to the Incomes Register: rewarding employees, payments made to an entrepreneur and other special circumstances
Read more about the 300 series income types
See the instructions for households paying non-wage compensations for work