Reporting data to the Incomes Register: households as employers
- Date of issue
- 12/4/2025
- Record no.
- VH/6669/05.00.00/2025
- Validity
- 1/1/2026 - Until further notice
These instructions are intended for households that pay wages or other earned income and report the data to the Incomes Register.
For a summary of the most important reporting-related matters, see Household as an employer.
The instructions describe
- the information required for reporting in the most common payment situations
- deadlines for reporting
- channels for reporting the information
- correcting reported information
- managing employer obligations
- examples of payment situations and reports.
These instructions apply to domestic situations. International situations are described in Reporting data to the Incomes Register: international situations.
These instructions replace the earlier instructions with the same name. The instructions have been updated:
- In Section 4.8.5, instructions have been added for a situation where the EUR 1,500 limit is exceeded in the middle of the year.
- In Section 5.2, a new example and a clarification has been added concerning the reporting of other payments when reporting wages.
Some technical specifications have also been made. In other respects, the contents of these instructions correspond to the previous instructions.
The amounts used in the examples are merely illustrative. Always withhold the tax in accordance with the income earner’s tax card. Check the amount of social insurance contributions each year from such sources as the websites of pension insurance providers or the Finnish Tax Administration.
The amounts used in the examples for the employee’s earnings-related pension insurance contributions and unemployment insurance contributions, and the employer’s health insurance contributions are at the 2023 level. The amounts valid for each year are provided on the insurance data page. The amount valid for employees aged under 53 and employees aged over 62 has been used as the amount of the employee’s earnings-related pension insurance contribution.
1 Households as employers
Households must report the following information to the Incomes Register:
- payments that they make (such as wages and fringe benefits)
- tax-exempt and taxable reimbursement of expenses
- certain non-wage compensation for work
- tax withholdings that they make.
Employee contributions collected from wages and insurance details must also be reported. There is no lower limit for the amount paid or any age limit for reporting. This means that you must report all wages and compensation you have paid, regardless of the amount or the age of the payment recipient.
A household means a private individual or a death estate.
For example, when you order a cleaning, babysitting or renovation service, you act as an employer. In that case, you must check the following:
- Are you paying wages or a non-wage compensation for work?
- If you are paying a non-wage compensation for work, is the recipient registered in the prepayment register?
- Do you need to withhold tax and pay the social insurance contributions?
- Are you a temporary employer or a contract employer?
- Are you a regular employer or a casual employer?
You can use the Finnish Tax Administration’s decision wizard to make the task easier. These matters are also covered in these instructions.
If you are not familiar with the terminology of the Incomes Register, take a look at the most important concepts.
1.1 Concepts of the Incomes Register
Income earner is an individual or a company to whom you make the payment.
An individual in an employment relationship is also called an employee or a wage earner. Income earners do not report their own income details to the Incomes Register. This information is always reported by the payer.
The payment is the amount of money that you pay to the income earner. It can be in the form of wages, non-wage compensation for work or a daily allowance.
In these instructions, the payer is the household that makes the payment to the income earner.
A household is a private individual or a death estate that hires an employee or purchases a service from a company or an individual.
A pool of household employers is an arrangement in which several households have jointly hired a cleaner, babysitter or other employee, and one individual pays the wages and submits the information to the Incomes Register on behalf of the pool using their own personal identity code.
An earnings payment report is a report on wages paid or other earned income submitted to the Incomes Register.
You must give the details of a single payment made to a single income earner on a single earnings payment report. A single earnings payment report can include several different income types.
Employer’s separate report is a report on the employer’s health insurance contribution submitted to the Incomes Register.
Even if you pay wages to more than one income earner, you only give one employer’s separate report each month.
Work performed for a household means work performed for an individual or death estate that is not related to the agricultural or business activities of this individual.
Income types mean the types of income on the basis of which the payments reported to the Incomes Register are itemised.
Income types include time-rate pay, contract pay, non-wage compensation for work and withholding tax.
Temporary employer and contract employer are concepts used by earnings-related pension insurance providers. They are used to determine whether the payer has concluded an agreement with an earnings-related pension insurance provider or not.
An employer must arrange the pension provision for its employees as a temporary employer or as a contract employer.
A regular employer must register in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register. Casual employers do not have any obligation to do this. Deadlines that a household must observe when submitting reports and its obligation to submit an employer’s separate report depend on whether or not the household is registered.
The payer is regarded as a casual employer if one of the following is true:
- The payer only has one permanent employee.
- The payer has up to five employees whose employment contracts do not cover an entire calendar year.
The payer is regarded as a regular employer in the following cases:
- The payer regularly pays wages to at least two employees.
- The payer regularly pays wages to one employee and also pays wages to at least one other employee, whose employment is fixed-term or meant to be short-term.
- The payer simultaneously pays wages to at least six employees, even if their employment contracts are fixed-term and meant to be short-term.
2 Reporting to the Incomes Register
Earnings payment data is only reported once, to one place. From the Incomes Register, the information is transmitted to such bodies as the Finnish Tax Administration, pension insurance providers and the Employment Fund. There is no monetary minimum threshold or age limit for reporting.
2.1 How do I submit a report?
You can calculate and pay wages in the free Palkka.fi service. The service automatically sends the information to the Incomes Register. If you use Palkka.fi, you do not need to submit any reports to the Incomes Register. Note that in Palkka.fi, you can only pay wages and that non-wage compensation for work cannot be paid in the service.
The Incomes Register also has its own e-service, which you can log in to at incomesregister.fi. In the e-service, you can submit one report at a time by entering the data on an online form. In the e-service you can report both wages and non-wage compensation for work.
If you use other payroll software than Palkka.fi, remember to check how to submit the reports to the Incomes Register. Some programs submit the data automatically but there is also software that compiles the data that you can then submit to the Incomes Register using the upload service of its e-service.
If you cannot use electronic services, you can submit the data on a paper form. You can print out the form at incomesregister.fi.
Take a look at different ways of reporting at Use our services electronically.
2.2 What is meant by a report and what information do I need for it?
When you pay wages or make other payments, you must prepare an earnings payment report on each individual and payment date separately. You must report both wages (Section 4) and non-wage compensation for work (Section 3) in the earnings payment report. The report on one individual may list several types of income as long as they all have the same payment date. You can report the withholding tax made from the income paid on the same date as a one-off payment.
If you have paid wages, also submit an employer’s separate report for the month in question in addition to the earnings payment reports. The details of the employer’s health insurance contribution are reported in the employer’s separate report. If you use Palkka.fi, the service submits both reports on your behalf.
Some of the information submitted in the earnings payment report is mandatory (always required) while some information is of supplementary nature (voluntary). Read more about the information required in different situations in Sections 3.1 (purchasing a service) and 4.2 (hiring an employee).
You must always give the details of the payer and the recipient (such as their names, identifiers and, in some cases, their addresses). When a household acts as an employer, the payer is always an individual or a death estate. Always give the personal identity code of the payer. This applies to both regular and casual employers. If you are a temporary employer, you must also give your first and last names, your address and the country code.
Enter Household as payer type. If you are reporting payments as a representative of a pool of household employers, see Section 6 for more detailed instructions.
Report all monetary amounts to the Incomes Register in gross amounts and to the cent.
If you are also purchasing agricultural work or business services, this work must be kept separate from the work you purchase as a household. You must always give your business ID on reports for agricultural work and business services. See Sections 4.3 and 4.4 for more information on reporting insurance details.
2.3 When should the data be reported?
The deadline for reporting the data depends on whether your household is a regular or a casual employer. Regular employers are registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register. The concepts of casual and regular employer are defined in the glossary at the beginning of these instructions.
If you are a casual employer, the deadline for submitting the electronic earnings payment report is the fifth day of the calendar month following the payment date. If you submit the report on a paper form, the deadline is the eighth day of the following month. If you have paid wages more than once during the month, report the wages you have paid on separate reports for each payment date.
Example 1: A casual employer pays wages
A household that is a casual employer pays wages twice in June (5 and 23 June), and once in September.
Separate earnings payment reports for both wage payments in June must be submitted electronically no later than 5 July or (on a paper form) no later than 8 July.
The report for the September wage payment must be submitted electronically no later than 5 October or (on a paper form) no later than 8 October.
If you are registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register (you are a regular employer), the deadline for submitting the electronic earnings payment report is the fifth calendar day following the payment date. If you submit the report on a paper form, the deadline is the eighth calendar day following the wage payment date.
Example 2: A regular employer pays wages
A household that is a regular employer pays wages on 15 June. The deadline for submitting the report on this wage payment is 20 June (electronic report) or 23 June (paper form).
If you need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution, the deadline for submitting the employer’s separate report electronically is the fifth day of the calendar month following the wage payment. If the report is submitted on a paper form, the deadline is the eighth day of the month following the wage payment.
- If you are a regular employer and do not pay wages during the month, you should only enter No wages payable in the employer’s separate report for this month. In that case, too, the deadline for submitting the employer’s separate report is the fifth day of the following month. For example, if no wages are paid in July, the deadline for submitting the report is 5 August (electronic report) or 8 August (paper form).
- If you are a casual employer, you only need to submit the employer’s separate report for the months in which you have paid wages or reimbursement of expenses.
There are a few exceptions to the general deadline for the earnings payment report:
- The deadline for reporting tax-exempt reimbursements of travel expenses (kilometre allowances, meal allowances and daily allowances) electronically is always the fifth day of the month following the payment month. If the report is submitted on a paper form, the deadline is the eighth day of the month following the wage payment.
- If you only grant the income earner a fringe benefit, you can report it monthly by the fifth day of the following month. If monetary wages are also paid during the month following the fringe benefit’s accrual month, you can also report the fringe benefit as income for the month following its accrual month. In that case, you must submit your report no later than the fifth day of the month following the month for which the fringe benefit has been reported as income.
- There are no specific deadlines for reporting voluntary information (see Section 4.2). We recommend that you submit the voluntary information together with the mandatory data whenever possible.
If you notice an error in the data you have reported, you must correct it by submitting a replacement report. In certain situations, a report containing errors must first be cancelled and a completely new report submitted afterwards. Read more about corrections in Section 7. There are no specific deadlines for submitting replacement earnings payment reports or replacement employer’s separate reports. However, you should correct the errors as soon as you notice them so that the erroneous information is not used when, for example, benefits are paid to the income earner.
Paper forms must arrive in the Incomes Register no later than the due date.
Saturdays, Sundays, and other holidays must be included when the fifth calendar day after the payment date is determined. However, if the report due date falls on a Saturday, Sunday or other holiday, the information can be reported on the following business day.
2.4 What happens if I submit the report after the deadline?
The Finnish Tax Administration will not impose any late filing penalty or negligence penalty for failures in reporting to the Incomes Register for individuals or death estates. However, other users of the Incomes Register data may impose sanctions.
3 A household purchases a service (pays a non-wage compensation for work)
If you purchase a service from a company or an individual and you do not conclude an employment contract, you are in a commission relationship with the company or individual in question. In such cases, the payment you make is always a non-wage compensation for work (and not wages).
Visit the BIS service or contact the Finnish Tax Administration to find out whether the service provider is registered in the prepayment register.
- If the service provider is registered in the prepayment register, you only need to pay the invoice for the work done, and you do not need to report the payment to the Incomes Register. See instructions on the tax credit for household expenses on the Finnish Tax Administration’s pages.
- If the service provider is not registered in the prepayment register, you must always report the non-wage compensation for work to the Incomes Register. You cannot pay or report non-wage compensation for work in the Palkka.fi service.
Typical non-wage compensation for work paid by households includes the compensation for renovation, cleaning or babysitting, and the compensation paid to a guardian.
3.1 Earnings payment report: information needed to report a non-wage compensation for work (the recipient is not registered in the prepayment register)
You must report the non-wage compensation for work that you pay in the earnings payment report if the recipient is not registered in the prepayment register. A non-wage compensation for work is usually paid against an invoice prepared by a company or an entrepreneur.
You need the following details for reporting the payment:
- payment date – the date on which the compensation arrives in the recipient’s account
- pay period – report the first working day as the start date and the last working day as the end date
- payer’s name and personal identity code – read more about identifiers in Section 2.2
- name and identifier of the recipient of the non-wage compensation for work (income earner); for example, personal identity code or business ID
- amount of the non-wage compensation for work without value added tax.
Specify the total amount as income type Non-wage compensation for work (336) to report the compensation. Include the share of the work (without value added tax), and travel expenses and other reimbursement of expenses itemised on the invoice in the total amount. Do not include other expenses (such as material expenses) itemised on the invoice in the non-wage compensation for work.
If you pay more than EUR 1,500 in non-wage compensation for work to the same individual or company during the calendar year, you must also withhold tax from the amount. In that case, you also need the recipient’s tax card and tax rate.
Withhold tax as follows:
- If you are paying a non-wage compensation for work to a business (general partnership, limited partnership, limited liability company or cooperative), withhold 13% in taxes from the share of work of the non-wage compensation for work and any reimbursement of travel expenses.
- If you are paying a non-wage compensation for work to a self-employed individual or other natural person, withhold tax from the share of work of the non-wage compensation for work according to the entrepreneur’s personal withholding rate.
- Withhold tax from the VAT-excluded share of the work. If the share of the work has not been itemised, withhold tax from the entire VAT-excluded amount.
- Specify the amount as income type Withholding tax (402).
If the EUR 1,500 limit is exceeded during the year, withhold tax and report the amount withheld to the Incomes Register in the report for the pay period during which the limit was exceeded (see Example 19, which also applies to withholding from non-wage compensation for work and reporting it). You do not need to withhold tax from non-wage compensation for work already paid.
Specify Household as additional payer information to ensure that the Finnish Tax Administration knows that the withholding limit stands at EUR 1,500. If the payer is a pool of household employers, see Section 6 for additional information.
Specify Corporate entity as additional income earner information if the recipient is a general partnership, limited partnership, limited liability company, cooperative, association, foundation or other legal person governed by private law. Do not report additional data if you pay the amount to a self-employed individual.
You do not need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution or other insurance contributions for non-wage compensation for work. The employer’s separate report is not required, and you do not need to report details of employment relationships, insurance policies or such matters as occupational class.
Services produced as mass services, designed and marketed for large consumer groups, are treated as the sales of goods, and payments made for them are not reported to the Incomes Register. Such services include public transport, healthcare services (including healthcare centre fees), hairdressing services, and restaurant/accommodation services. However, payments for charter transport and catering services are non-wage compensation for work that must be reported to the Incomes Register.
3.2 Examples of reporting non-wage compensation for work
A variety of different reporting situations is described in the examples. The examples do not contain all the data included in the reports. See the examples of wages (Section 4.8) on how to report the payer’s and recipient’s identification data and general information (such as payment date and payment period).
Example 3: A non-wage compensation for work paid to an entrepreneur registered in the prepayment register
The household pays a non-wage compensation for work of EUR 2,000, a kilometre allowance of EUR 200 and a taxable reimbursement of expenses of EUR 35 for work equipment to a self-employed individual registered in the prepayment register for renovation work.
Because the entrepreneur is registered in the prepayment register, the payment is not reported to the Incomes Register.
Example 4: A non-wage compensation for work paid to an entrepreneur who is not registered in the prepayment register
The household pays a non-wage compensation for work of EUR 2,000, a kilometre allowance of EUR 200 and a taxable reimbursement for expenses of work equipment of EUR 35 for renovation work to a self-employed individual who is not registered in the prepayment register.
Because the entrepreneur is not registered in the prepayment register, the paid income must be reported to the Incomes Register on an earnings payment report.
The payer calculates the total of the compensation and kilometre allowances and reports the total in the earnings payment report specifying Non-wage compensation for work (336) as the income type. No tax needs to be withheld from the kilometre allowances because they are related to a non-wage compensation for work received by a natural person. The Finnish Tax Administration has decided that such reimbursements of travel expenses are exempt from withholding. The payer calculates the withholding based on the combined total of compensation and work equipment (EUR 2,035). According to the entrepreneur’s tax card, the withholding rate is 25%.
In addition to the payer’s and recipient’s identifying information, the following data must also be reported:
| REPORT DETAILS | EUR |
|---|---|
| Payer type: Household | |
| 336 Non-wage compensation for work | 2235.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax (from EUR 2,035) | 508.75 |
Example 5: A non-wage compensation for work is paid to a company that is not registered in the prepayment register
The household pays an invoice of EUR 15,000 for earthmoving work to a limited liability company that is not registered in the prepayment register.
The work and materials are itemised in the invoice. Ordered work accounts for EUR 5,000 of the total, and materials (such as crushed stone and gravel) account for the remaining EUR 10,000. Work (excl. VAT) accounts for EUR 4,032.26 of the work. The payer withholds 13% from the VAT-free price of the work. The payer reports the VAT-free share of the work and the taxes withheld from the sum in the earnings payment report.
In addition to the payer’s and recipient’s identifying information, the following data must also be reported:
| REPORT DETAILS | EUR |
|---|---|
| Payer type: Household | |
| Additional income earner information: Organisation | |
| 336 Non-wage compensation for work | 4032.26 |
| 402 Withholding tax (from EUR 4,032.26) | 524.19 |
Example 6: Compensation and kilometre allowance paid to a guardian
A guardian has been paid a compensation of EUR 1,600 and a kilometre allowance of EUR 200.
The compensation and kilometre allowance must be reported as a total sum as income type Non-wage compensation for work (336). The guardian may claim work-related costs as deductions in their own taxation. A withholding of 20% is made from the compensation based on the guardian’s tax card.
In addition to the payer’s and recipient’s identifying information, the following data is also reported:
| REPORT DETAILS | EUR |
|---|---|
| Payer type: Household | |
| 336 Non-wage compensation for work | 1800.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax (from EUR 1,600) | 320.00 |
3.3 The household orders services via a platform or an application
A wide range of different services is offered via mobile applications and platforms operating in the internet. The services can involve any kind of work, such as renovation work, cleaning services, pet grooming or walking, making deliveries for various restaurants, or organising experiences for tourists.
Employment services and ordering of services via applications and platforms may involve various responsibilities applying to the worker, the application owner, or the client, i.e., the party who purchases a service or commissions work via an application or a platform. Some applications and platforms may mostly act as electronic bulletin boards, meaning that the worker and the client must agree on the terms and conditions of the work between them. Some applications and platforms, however, function so that an employment relationship is automatically established between the worker and the client, but the platform handles the payment traffic. An employment relationship can also be established between the worker and the platform. The obligation to report the payments to the Incomes Register depends on what has been agreed between the application or platform, the worker and the client.
This means that if your order services via a platform, an employment or commission relationship may be established between you and the employer. In that case, you must report the payments you have made to the Incomes Register as wages or non-wage compensation for work, depending on what has been agreed. Non-wage compensation for work must only be reported if the payment recipient is not registered in the prepayment register. The date on which you made the payment to the platform or other application must be given as the payment date.
Example 7: You are using a platform to pay a non-wage compensation for work to an individual who is not registered in the prepayment register
Peter offers dog-walking services via a platform. A pet owner (household) makes a reservation and enters their payment details to the platform. A sum of EUR 100 is taken from the pet owner’s account when Peter has confirmed that he accepts the job offer. After Peter has completed the work, the platform pays Peter a compensation of EUR 80 and deducts the platform fee (EUR 20) from the payment. The platform only acts as an employment agency between Peter and the pet owner. Peter is in a commission relationship with the pet owner.
Because Peter is not registered in the prepayment register, the pet owner must report the paid non-wage compensation for work to the Incomes Register. The pet owner reports the entire EUR 100 payment on an earnings payment report, specifies Peter as the income earner and enters the date when making the payment to the platform as the payment date. Because the payer is a household, the report must be submitted no later than the fifth day of the month following the payment date. In his own taxation, Peter can request that the platform fee of EUR 20 should be deducted as expenses for the production of income.
4 Employing an individual to work for a household
If you have concluded an employment contract with an employee, you must pay wages to this employee. In that case, you must manage an employer’s obligations, which include
- tax withholding
- taking out of earnings-related pension insurance
- taking out of accident and occupational disease insurance
- payment of unemployment insurance contributions
You can also check your obligations as an employer by answering the questions asked in the Finnish Tax Administration’s decision wizard.
Examples of reporting wages paid in different situations can be found in Section 4.8. If you hire a babysitter and receive private daycare allowance from Kela, see Section 5 for more information.
4.1 Social insurance contributions and withholding of taxes
The employer’s obligations also depend on the amount of the wages and the employee’s age. If you are not obliged to take out insurance for the employee, this must also be mentioned in the report.
The chart below describes how the wages you pay as a household impact your obligations. The euro limits apply to 2026.
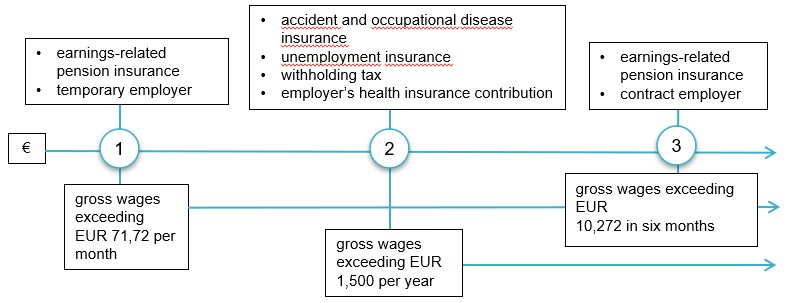
When the wages you pay exceed one of the limits specified above, you must fulfil the respective obligation, such as taking out insurance for the employee and pay the insurance contributions.
1. If you pay more than EUR 71,72 in gross wages per month, you must take out earnings-related pension insurance for the employee. If you do not employ anybody on a permanent basis, you can manage your pension insurance obligations as a temporary employer (without an agreement with the pension insurance provider).
You do not need to take out other insurance policies or pay any insurance contributions. Note however that the employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution must also be collected from the employee when the maximum sum paid in wages is EUR 1,500. In that case, the employer ends up with the unemployment insurance contribution. The income earner receives the collected amount as a deduction from their own taxation.
2. If you pay a gross wage of more than EUR 1,500 to one or more employees during a calendar year, you must take out accident and occupational disease insurance for them and pay unemployment insurance contributions.
If you pay one employee a gross wage of more than EUR 1,500 per year, you must withhold tax from the wages and pay the employer’s health insurance contribution. If requested by the employee, tax can also be withheld from wages that are below this level. You must report all withholding tax to the Incomes Register.
If the EUR 1,500 limit is exceeded during the year, you must withhold tax and pay the employer’s health insurance contribution from the month during which the limit was exceeded. You only need to make the withholding from the part exceeding EUR 1,500, but the health insurance contribution must be based on the whole year’s payments.
3. If you pay more than EUR 10,272 in gross wages during six consecutive months or you have an individual in a permanent employment relationship, you must take out insurance from an earnings-related pension provider. In that case, you are a contract employer and no longer a temporary employer. Even if the wages you pay remain under this limit, you can still become a contract employer if you wish and take out pension insurance from an earnings-related pension provider.
Read more about reporting earnings-related pension insurance data and acting as a temporary employer in Section 4.4.
Different types of insurance have different age limits.
- The employer’s health insurance contribution must be paid for employees aged 16 and over, and for employees up to the age of 67.
- The employee’s unemployment insurance contribution must be paid for employees aged 18 and over, and for employees up to the age of 64.
- Earnings-related pension insurance must be taken out for employees aged 17 and over. The insurance obligation ends when the employee reaches the age of
- 68 (if they were born in or before 1957)
- 69 (if they were born between 1958 and 1961)
- 70 (if they were born in or after 1962).
- There are no similar age limits for accident and occupational disease insurance.
In all insurance categories, the obligation starts from the beginning of the month following the month when the employee reaches the lower age limit. The obligation ends at the end of the month during which the employee reaches the age of 68 (health insurance and earnings-related pension insurance) or 65 (unemployment insurance).
If you do not have any obligation to take out insurance you must list the insurance categories concerned in income earner information under No obligation to take out insurance. Read more in Examples 12–15.
Withholding tax and the employer’s health insurance contribution are self-assessed taxes, which you must calculate and pay yourself. Other social insurance contributions are paid using the invoicing method used by the insurance provider.
If you have taken out pension and occupational accident insurance policies, you must always give the name and personal identity code of the household member that has taken out the policies. The data must be entered under payer details.
You can find more information on
- the obligation to withhold tax and the employer’s health insurance contribution in the Finnish Tax Administration’s instructions Household’s obligations as an employer.
- taking out pension insurance in the Finnish Centre for Pensions’ earnings-related pension legislation service (the information is in Finnish) and on the websites of individual pension insurance providers
- taking out accident and occupational disease insurance on the Finnish Workers’ Compensation Center’s website
- the obligation to pay unemployment insurance contributions on the Employment Fund’s website.
- If you do not have internet access, you can contact these bodies personally.
4.2 Earnings payment report: data needed to report wages
Use the earnings payment report to report the wages, fringe benefits and other compensation you have paid.
You need the following data for reporting the payments:
- payment date (the date on which the wages arrive in the recipient’s account)
- pay period; report the first working day as the start date and the last working day as the end date
- payer’s name and personal identity code; read more about identifiers in Section 4.3 and see Section 6 if the payer is a pool of household employers
- name and identifier of the recipient (for example, personal identity code or business ID)
- gross pay and any fringe benefits (read more about wage income types in Section 4.5).
You may also require the following information:
- details of insurance policies (read more about earnings-related pension insurance in Section 4.4)
- occupational class; if you are obliged to take out accident and occupational disease insurance for your employees, you get the details of the occupational classes from your accident insurance provider
- recipient’s tax card and tax rate (if you withhold tax from the wages).
We recommend that you report all the information concerning the employment relationship. If the information is incomplete or contrary to the instructions in the Incomes Register, the income earner may be awarded a benefit on the wrong grounds or in the wrong amount, the decision on the benefit may be delayed (often a request for further clarification to the data submitter) or the taxation of the income earner may be incorrect.
The following data items are always voluntary for a household acting as an employer:
- whether the employment is full-time or part-time, valid until further notice or fixed term
- type of payment (monthly salary, hourly wages or contract pay)
- paid and unpaid absences and reasons for them, wages paid during a paid absence
- the earnings periods of the income types.
If the employee retires on an old-age pension, the time of employment and the reason for the end of employment (retirement) are mandatory data.
We recommend that you report the voluntary data together with the wage and mandatory data to ensure that the authorities do not need to request the information later.
If you need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution, you must submit the employer’s separate report in addition to the earnings payment report. For further instructions, see Section 4.6 Employer’s separate report on employer’s health insurance contribution.
4.3 Identifiers of payer and income earner
When a household acts as an employer, the payer is always an individual or a death estate. Always give the personal identity code of the payer. We recommend that you always also indicate the name of the payer. Based on the name, the party using the information can, for example target the other pay reports correctly. Specify as the payer the member of the household who has taken out the pension and occupational accident insurance policies.
If you are also purchasing agricultural work or business services, this work must be kept separate from the work you purchase as a household. You must always give your business ID on reports for agricultural work and business services. If separate pension and occupational accident insurance policies have been taken out for agricultural work or business services, make sure that you use the correct insurance details, including the pension policy number and insurance policy number, in the reports.
If both spouses act as employers, both have the obligation to report their own payments to the Incomes Register. The monetary limits for employer’s obligations apply individually to each payer.
A household may have a guardian or agent who, in practice, handles data reporting and wage payments on behalf of the household. The client (the household) remains responsible for ensuring that the data is reported to the Incomes Register. In such cases, too, the household is entered as the payer. An underage person can be the payer using their own income.
Specify Household as payer type to ensure that the Finnish Tax Administration knows that there is a EUR 1,500 limit to the household’s obligation to withhold tax and pay the employer’s health insurance contribution. If you are reporting payments as a representative of a pool of household employers, see Section 6 for more detailed instructions.
4.4 Earnings-related pension insurance, temporary employer and YEL insurance
If you pay the employee a gross wage of less than EUR 71,72 per month (in 2026), you do not need to take out earnings-related pension insurance for the employee. The employee’s age is irrelevant. However, small wages must also be reported to the Incomes Register. See Example 12 on reporting small wages.
If you pay the employee a gross wage of at least EUR 71,72 per month (in 2026), you must take out earnings-related pension insurance for the employee. Whether or not you are obliged to take out the insurance depends on the age of the employee (for age limits, see Section 4.1).
You can manage your earnings-related pension insurance obligation as a temporary employer or as a contract employer.
You can manage your earnings-related pension insurance obligation as a temporary employer if you pay an individual a gross wage of no more than EUR 10,272 over a period of six consecutive months (in 2026) and you do not have permanent employees. The turn of the calendar year will not interrupt the calculation of the six-month time limit. As a temporary employer, you do not have a valid insurance policy with an earnings-related pension insurance provider.
In that case, you must give the following details of the payer and insurance in the earnings payment report:
- Payer type: Household (if necessary, also Pool of household employers).
- Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy). In the Incomes Register e-service, information about temporary employer must be reported in the income earner’s insurance data.
- Details of earnings-related pension insurance: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance.
- Earnings-related pension provider code: You can select the pension provider yourself. The pension provider will send you an invoice based on the data you have submitted.
- If you report the data in the Incomes Register’s e-service, choose the earnings-related pension provider from the menu.
- If you submit the report on a paper form, give the earnings-related pension provider code.
- If you are reporting the data via API or in an upload service, you must enter the pension policy number (technical insurance policy number) in addition to the code. You should request the pension policy number from the earnings-related pension provider.
- Payer’s name: your first and last names.
- Payer’s address and address country code (for example: FI for Finland).
If you wish, you can take out an earnings-related pension insurance policy, even if the limit of EUR 10,272 is not exceeded. However, you must always take out pension insurance if you have an individual in a permanent employment relationship or you pay more than EUR 10,272 in wages over a period of six consecutive months (in 2026). In that case, you can no longer be a temporary employer.
If your status changes from a temporary employer to a contract employer, you must give the following payer and insurance data in the earnings payment report from the next wage payment:
- Payer type: Household (if necessary, also Pool of household employers)
- Details of earnings-related pension insurance: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance.
- Earnings-related pension provider code: code of the pension provider where you have taken out the insurance.
- Pension policy number: you get the number from the pension provider where you have taken out the insurance.
In both cases, you must use income type Employee’s pension insurance contribution (413) to report the pension insurance contribution you have collected from the wages. See Examples 15–19 on reporting wages as a temporary employer.
Also consider the following when paying the pension insurance contribution:
- If you are using the Palkka.fi service, you can choose the earnings-related pension provider and pay the pension insurance contribution as you calculate the wages. The Palkka.fi service will automatically send a report to the Incomes Register.
- If you pay wages to an employee in an employment relationship and the employee has pension insurance for the self-employed (YEL) on the basis of their other activities, you must pay the employee’s pension insurance contribution. YEL insurance does not affect a household employer’s insurance obligations.
- However, if the individual is a YEL-insured entrepreneur to whom you pay a non-wage compensation for work, see more detailed instructions in Section 3. If the entrepreneur is not registered in the prepayment register, you do not need to pay the TyEL contribution, but you must withhold tax from the non-wage compensation for work.
4.5 Wage income types and using them
You must report to the Incomes Register all wages and other payments that you have paid. The information must be submitted, even if the wages were small or even if you had not withheld any tax from them. Reporting is also required irrespective of whether or not you must pay social insurance contributions on the wages.
See Section 4.8 for examples of reports containing all mandatory data. The income type examples only contain the details of the income types used.
4.5.1 Monetary wages
You can report monetary wages in the Incomes Register in two different ways.
Mandatory minimum level is the reporting method 1: Report monetary wages as total sum (income type 100 series). You can include all income types of 200 series in income type Total wages (101), such as time-rate pay, contract pay and overtime compensation.
Reporting method 2 is an alternative to method 1: Report monetary wages in an itemised manner (income type 200 series). In that case, the wages comprise the income you have reported (such as hourly pay, overtime compensation and holiday bonus), and you do not need to calculate the total income.
Note that certain income categories and payments must always be reported as specific income types if they have been paid, or deducted from wages. These include fringe benefits, reimbursement of expenses and other separately reported income (300 series).
Likewise, the tax withholdings you have made and the employee’s pension insurance and unemployment insurance contributions you have paid must always be reported as specific income types (400 series). They must be itemised, even if you report the monetary wages as a total sum. This means that such income as fringe benefits cannot be included in the total wage sum. However, you can calculate the total of the withholding tax from the income of the same payment date and report it as a single sum.
Reporting methods 1 and 2 cannot be used simultaneously in the same report. However, you are free to change reporting methods between reports.
We recommend that you report monetary wages in an itemised manner using reporting method 2. In that case, all users of Incomes Register data get the data they need straight away and they do not need to request information from you for such purposes as decisions on benefits payable to income earners.
Also note that if you use reporting method 1 and if the amount of income type 101 is only partially subject to social insurance contributions, you must also use income subtypes 102–106 in the reporting. It is simpler to report insurance data with reporting method 2. Read more in Section 1.3 (Type of insurance data) of instructions Reporting data to the Incomes Register: insurance-related data.
Example 8: Reporting monetary wages as a total sum or in an itemised manner
The household pays a housekeeper EUR 2,600 in wages as a one-off payment. The housekeeper receives a monthly pay of EUR 2,100 and a holiday bonus of EUR 500.
The payer can report the monetary wages in two different ways. Withholding and the insurance contributions collected must be reported separately in both methods.
Only the use of income types is described in this example. Report the wages as follows:
| MANDATORY MINIMUM LEVEL | ALTERNATIVE METHOD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reporting method 1 | EUR | Reporting method 2 | EUR |
| 101 Total wages | 2600.00 | 201 Time-rate pay | 2100.00 |
| 213 Holiday bonus | 500.00 | ||
| 402 Withholding tax | 650.00 | 402 Withholding tax | 650.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 185.90 | 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 185.90 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 39.00 | 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 39.00 |
Report the wages as income type Time-rate pay (201) if they are paid according to hourly or weekly rates, for example. Report the wages as income type Contract pay (227) if they are paid based on a contract.
4.5.2 Fringe benefits
Fringe benefits include accommodation, meal and car benefit. The Tax Administration issues an annual decision in which it sets the values of fringe benefits.
If you grant an employee fringe benefits, you must withhold tax from the total amount of monetary wages and fringe benefits. However, the withholding may not exceed the amount of the monetary wages. If you only grant fringe benefits and do not pay any other compensation, no tax can be withheld.
Fringe benefits are considered as wages, which means that they affect the calculation of the employer’s health insurance contribution and other social insurance contributions. Read more about reporting fringe benefits in instructions Reporting data to the Incomes Register: fringe benefits and reimbursement of expenses.
Example 9: The household grants a meal benefit to an employee
In addition to paying wages, a household also grants an employee a meal benefit of EUR 150.
The payer can report the meal benefit in two ways: as income type Meal benefit (334) or as total fringe benefits under income type Other fringe benefit (317). The benefit type must also be given when the total benefit is reported: Meal benefit. If the payer reports the benefit as a separate income type, it can no longer be added to income type Other fringe benefit (317).
The payer makes a withholding from the value of the meal benefit and pays social insurance contributions if the prerequisites described in Section 4.1 are met. Wage income types and items deducted from wages are not included in the example; see Example 8 for information on reporting them.
Fringe benefits are reported as follows:
| SEPARATELY REPORTED INCOME TYPES | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Mandatory minimum level |
EUR |
Alternative method |
EUR |
|
317 Other fringe benefit Type of benefit: Meal benefit |
150.00 |
334 Meal benefit |
150.00 |
The payer could also report accommodation and telephone benefits as separate income types or as a total sum. Certain fringe benefits (such as car benefit) must always be reported as separate income types.
Read more in instructions Reporting data to the Incomes Register: fringe benefits and reimbursement of expenses.
4.5.3 Tax-exempt reimbursement of travel expenses
Tax-exempt reimbursement of travel expenses include meal allowance, kilometre allowance, and various daily allowances. You can pay these reimbursements for work-related travel expenses.
Each year, the Tax Administration issues a decision specifying the prerequisites for the tax-exempt status of reimbursement of travel expenses. If these prerequisites are not met, the reimbursements are deemed as wages to their full amount. In that case, you must report them to the Incomes Register as wages. If the reimbursements you pay exceed the tax-exempt maximum, you must report the excess amount as wages.
If the employee is in a commission relationship instead of an employment relationship (you purchase a service from this employee; see Section 3), you cannot pay tax-exempt reimbursements. In that case, you must report the reimbursements you have paid as non-wage compensation for work (see Example 4).
Example 10: The household pays a daily allowance, meal allowance and kilometre allowance
In addition to wages, a household pays the employee a daily allowance of EUR 144, a meal allowance of EUR 12 and a kilometre allowance of EUR 79.50.
The payer can report the meal allowance as income type Meal allowance (303) or as a total sum (meal allowance + daily allowance) under income type Daily allowance (331).
The type of daily allowance must always be given. In this example, it is Meal allowance, Full daily allowance or both (depending on the reporting method). If the payer reports the meal allowance as a separate income type, it can no longer be added to income type Daily allowance (331). Kilometre allowance must always be reported as a separate income type.
Wage income types are not included in the example; see Example 8 for information on reporting them.
Reimbursements of expenses are reported as follows:
| SEPARATELY REPORTED INCOME TYPES | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Mandatory minimum level |
EUR |
Alternative method |
EUR |
|
331 Daily allowance Type of daily allowance: Meal allowance Type of daily allowance: Full daily allowance |
156.00 |
331 Daily allowance Type of daily allowance: Full daily allowance |
144.00 |
|
|
303 Meal allowance |
12.00 |
|
|
311 Kilometre allowance (tax-exempt) Number of kilometres: 150* |
79.50 |
311 Kilometre allowance (tax-exempt) Number of kilometres: 150* |
79.50 |
* Kilometres travelled can be given for each pay period. However, this information must be given on the last report of the year at the latest.
4.5.4 Taxable reimbursement of expenses
Taxable reimbursement of expenses is used to compensate for costs directly incurred by employees
- from carrying out their work tasks (such as purchases of work equipment and materials)
- if these costs are not included in the reimbursement of travel expenses.
Even though these reimbursements of expenses are taxable, they are not considered as wages when tax is withheld. This means that the payer should not add them to the reported wages when using such income types as Time-rate pay (201). Likewise, no social insurance contributions are paid or reported on them.
Reimbursement of costs that have not been reported as other income types and from which no tax has been withheld are reported as income type Taxable reimbursement of expenses (353).
Example 11: The household pays a reimbursement of expenses for work equipment
The household pays a construction worker EUR 35 as reimbursement of expenses for work equipment based on the collective agreement. No taxes are withheld or social insurance contributions paid from this reimbursement. The monetary amount of the reimbursement is reported as income type Taxable reimbursement of expenses (353).
The reimbursement is reported as follows:
| SEPARATELY REPORTED INCOME TYPES | EUR |
|---|---|
| 353 Taxable reimbursement of expenses | 35.00 |
4.6 Employer’s separate report on the employer’s health insurance contribution
If you pay a gross wage of more than EUR 1,500 to the same employee during a calendar year, you must pay the employer’s health insurance contribution and report it to the Incomes Register in the employer’s separate report.
You do not need to pay the contribution if the wages remain under this limit. Likewise, if you have two employees and pay each of them EUR 1,000 in wages, you do not need to pay the contribution on the basis of these payments.
The employer’s health insurance contribution is paid for employees aged between 16 and 67. You must calculate the employer’s health insurance contribution on the basis of the gross wages you have paid each month. In addition to monetary wages, gross wages also include fringe benefits.
You must report the total amount of the employer’s health insurance contribution in the employer’s separate report. Do not enter the total amount of gross wages in the report. Submit only one employer’s separate report for each wage-payment month. See Section 2.3 for deadlines for submitting employer’s separate reports.
You can also pay and report the employer’s health insurance contribution for wages less than EUR 1,500 if you know that the employee’s gross wages will later exceed the limit. In that case, submit the separate report in accordance with each pay period.
If you have not paid the employer’s health insurance contribution before the EUR 1,500 limit was exceeded and the limit is exceeded later in the year, you must calculate and pay the sum based on the amount of gross wages for the entire year. Report the employer’s health insurance contribution payable from the full year’s wage amount as a total sum in the separate report of the month in which the annual limit of EUR 1,500 is exceeded.
Give the following information in the employer’s separate report:
- name and personal identity code of the payer, report contact person, reporting date and reporting period (payment month and payment year)
- payer type Household
- payer types Household and Pool of household employers if you report the information on behalf of a pool of household employers
- employer’s health insurance contribution in total if wages have been paid
- any deductions you have made from the total amount of the health insurance contribution
- Enter No wages payable if you are a regular employer (registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register) and you have not paid any wages during the month in question.
Read more and see examples in Section 6 of instructions Reporting data to the Incomes Register: employer’s separate report: When does a household submit the employer’s separate report?
If you only pay a non-wage compensation for work, you do not need to pay or report the employer’s health insurance contribution.
4.7 Payment of wages and employer’s contributions
When you hire an employee, remember to take care of the following:
- Pay wages to the employee as agreed.
- Pay the taxes you have withheld from the wages and the employer’s health insurance contributions to the Finnish Tax Administration in MyTax or in your online bank no later than the 12th day of the month following the payment month.
- Pay any earnings-related pension and accident and occupational disease insurance contributions to the insurance providers of your choice and the unemployment insurance contributions to the Employment Fund. The earnings-related pension insurance providers will invoice the contributions directly from you unless otherwise agreed.
If you calculate and pay the wages in the Palkka.fi service, the service will automatically generate the payment details for withholding, employer’s health insurance contribution, and earnings-related pension insurance contribution, which you can use when paying the amounts in your online bank.
The unemployment insurance contribution cannot be paid in the Palkka.fi service. The Employment Fund will impose the payment when the wage amount exceeds EUR 1,500 in a calendar year. Accident and occupational disease insurance contributions cannot be paid in the Palkka.fi service either. The insurance providers will invoice the contributions separately.
Instructions for payment can be obtained from the websites of the Finnish Tax Administration, insurance providers, and the Employment Fund, or by contacting these bodies.
4.8 Examples of reporting wages
The examples describe a variety of different reporting situations. The employer obligations also depend on the amount of the wages and the employee’s age. Read more in Section 4.1.
Monetary wages are reported in the examples in an itemised manner (income type 200 series). We recommend that you always use this reporting method, as it is more accurate.
4.8.1 Gross wage is less than EUR 71,72 per month
When the wages paid are small or the employee is young, you only need to take out a limited number of insurance policies. If you do not need to take out a specific insurance, you must state this in the report by entering No obligation to take out insurance.
Example 12: The household pays EUR 40 to an individual aged 15
The household pays EUR 40 to an individual aged 15 as a one-off payment. There are no other employees and no other wages are paid during the year.
The wages are so low that the household is not obliged to pay social insurance contributions. For this reason, the household enters No obligation to take out insurance for all insurance policies. No withholding tax is required. Because the household does not need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution, the employer’s separate report is not required either.
The household reports the following data to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 20.01.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.01.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.01.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy)* Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (earnings-related pension, health, unemployment or accident and occupational disease insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay* | 40.00 |
* Report the wages as income type Time-rate pay if you are paying the wages based on an hourly rate, for example. Report the wages as income type Contract pay if you are paying the wages based on a contract.
Example 13: The household pays EUR 40 to an individual aged 19
The household pays EUR 40 to an individual aged 19 as a one-off payment. There are no other employees and no other wages are paid during the year.
The wages are so low that the household is not obliged to pay social insurance contributions. Because the employee is aged over 18, the household must, however, collect the employee’s unemployment insurance contribution from the wages. In that case, the employer ends up with the unemployment insurance contribution. The household enters No obligation to take out insurance for all other insurance policies except for the unemployment insurance.
No withholding tax is required. Because the household does not need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution, the employer’s separate report is not required either.
The household reports the following data to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 20.01.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.01.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.01.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (earnings-related pension insurance) No obligation to provide insurance (health insurance) No obligation to provide insurance (accident and occupational disease insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay* | 40.00 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution ** | 0.60 |
* Report the wages as income type Time-rate pay if you are paying the wages based on an hourly rate, for example. Report the wages as income type Contract pay if you are paying the wages based on a contract.
** As an employer, you must always withhold the employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution from the wages, even if you are not required to pay the employer’s share. In that case, the employer ends up with the unemployment insurance contribution you have collected. The income earner receives the collected amount as a deduction from their own taxation.
The type of exception to insurance ‘No obligation to take out insurance (unemployment insurance)’ is used when the employee is aged under 18 or over 65.
4.8.2 Maximum gross wage of EUR 1,500 per year
When you are paying wages as a household in excess of the lower limit specified in the earnings-related pension insurance scheme but no more than EUR 1,500 per year, your insurance obligations partially depend on the employee’s age.
Example 14: The household pays EUR 400 to an individual aged 15
The household pays EUR 400 in wages to a 15-year-old neighbour as a one-off payment for caring for school-aged children. The family is not eligible for private daycare allowance. The household is a temporary employer and is not registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register.
The work was performed in July and the wages were paid on 2 August. No tax is withheld in this example. There are no other employees and no other wages are paid during the year.
Because the income earner is aged 15, the income paid is not used as a basis for earnings-related pension, unemployment or health insurance contributions. Neither is the accident and occupational disease insurance contribution paid because the wages paid by the household are less than EUR 1,500 per year. For these reasons, the household enters No obligation to take out insurance for all insurance policies.
Because the household does not need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution, the employer’s separate report is not required either.
The household reports the following data to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 02.08.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.07.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.07.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (earnings-related pension, health, unemployment or accident and occupational disease insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay* | 400.00 |
* Report the wages as income type Time-rate pay if you are paying them based on an hourly rate, for example. Report the wages as income type Contract pay if you are paying the wages based on a contract.
The household can also report the occupational class if it so wished. Reporting it is recommended if the income earner is in an employment relationship. The occupational class must be given if the income earner is covered by occupational accident insurance and receives earnings subject to the occupational accident insurance contributions. See Example 17 for information on reporting the occupational class.
Example 15: The household pays EUR 350 to an individual aged 18
The household pays EUR 350 in wages to an individual aged 18 as a one-off payment for caring for school-aged children. The family is not eligible for private care allowance. The household is a temporary employer and is not registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register.
The work was performed in June and the wages were paid on 15 June. No tax is withheld in this example. There are no other employees and no other wages are paid during the year.
Because the income earner is aged over 18, the household must take out pension insurance and pay the earnings-related pension insurance contribution. Based on the age, the wages are also subject to an unemployment insurance contribution but the limit of EUR 1,500 is not exceeded. However, the household must collect the employee’s unemployment insurance contribution from the wages. In that case, the employer ends up with the unemployment insurance contribution.
In addition to the wages, the household must also report the earnings-related pension insurance contribution and the unemployment insurance contribution.
As less than EUR 1,500 is paid in wages, the wages are not subject to the health insurance contribution or the accident and occupational disease insurance contribution. For this reason, the household enters No obligation to take out insurance for these two contributions.
The household reports the following data to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 15.06.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.06.20xx The end date of the pay period: 15.06.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code*: NN Pension policy number**: NNNNNNN Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (accident and occupational disease insurance) No obligation to provide insurance (health insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay* | 350.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 25.02 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution **** | 5.25 |
* Earnings-related pension provider code: Select a pension provider and give its code. Examples below:
- 46 Ilmarinen Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 54 Elo Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 55 Varma Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 56 Veritas Pension Insurance Company
** If you are a temporary employer and submit the report in the Incomes Register’s e-service or on a paper form, you do not need to provide the pension policy number. The number is only required if you submit the report via API or in an upload service.
*** Report the wages as income type Time-rate pay if you are paying the wages based on an hourly rate, for example. Report the wages as income type Contract pay if you are paying the wages based on a contract.
**** As an employer, you must always withhold the employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution from the wages, even if you are not required to pay the employer’s share. In that case, the employer ends up with the unemployment insurance contribution you have collected. The income earner receives the collected amount as a deduction from their own taxation.
The household can also report the occupational class if it so wished. Reporting it is recommended if the income earner is in an employment relationship. The occupational class must be given if the income earner is covered by occupational accident insurance and receives earnings subject to the occupational accident insurance contribution. See Example 17 for information on reporting the occupational class.
Example 16: The household pays EUR 1,000 to an individual aged 30
The household pays EUR 1,000 in wages to an individual aged 30. There are no other employees and no other wages are paid during the year.
The earnings-related pension insurance contribution and employee’s unemployment insurance contribution must be paid and reported for the employee. No tax is withheld in this example. Because the household does not need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution, the employer’s separate report is not required either.
The employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution must always be collected from the employee, even if the employer has no payment obligation because the EUR 1,500 limit applied to the employer is not exceeded.
The household reports the following data to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 15.06.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.06.20xx The end date of the pay period: 30.06.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code*: NN Pension policy number**: NNNNNNN Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (accident and occupational disease insurance) No obligation to provide insurance (health insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay*** | 1000.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 71.50 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution **** | 15.00 |
* Earnings-related pension provider code: Select a pension provider and give its code. Examples below:
- 46 Ilmarinen Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 54 Elo Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 55 Varma Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 56 Veritas Pension Insurance Company
** If you are a temporary employer and submit the report in the Incomes Register’s e-service or on a paper form, you do not need to provide the pension policy number. The number is only required if you submit the report via API or in an upload service.
*** Report the wages as income type Time-rate pay if you are paying the wages based on an hourly rate, for example. Report the wages as income type Contract pay if you are paying the wages based on a contract.
**** As an employer, you must always withhold the employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution from the wages even if you are not required to pay the employer’s share. In that case, the employer ends up with the unemployment insurance contribution you have collected. The income earner receives the collected amount as a deduction from their own taxation.
The household can also report the occupational class if it so wished. Reporting it is recommended if the income earner is in an employment relationship. The occupational class must be given if the income earner is covered by occupational accident insurance and receives earnings subject to the occupational accident insurance contribution. See Example 17 for information on reporting the occupational class.
4.8.3 Maximum gross wage of EUR 1,500 per year
When you are paying more than EUR 1,500 in wages per year as a household, you must, as a rule, withhold tax from the wages, take out earnings-related pension insurance, accident and occupational disease insurance, and pay unemployment insurance contributions. You must also pay employer’s health insurance contribution and report it in the employer’s separate report.
Example 17: The household pays EUR 1,600 for renovation as a temporary employer
The household is a temporary employer and pays EUR 1,600 in wages for a renovation. There are no other employees.
The unemployment insurance contribution and accident and occupational disease insurance contribution must be paid for the employee in addition to the earnings-related pension insurance contribution and employer’s health insurance contribution. Taxes must also be withheld from the wages and the withholding must be reported.
The wages can be reported as income type Time-rate pay or Contract pay, for example, depending on whether the work was agreed to be performed using an hourly rate or for a contract price.
The household reports the following data to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 20.01.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.01.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.01.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy)* Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class**: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code***: NN Pension policy number****: NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay | 1600.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax | 640.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 114.40 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 24.00 |
* If the household is a contract employer (has taken out insurance from a pension provider) nothing needs to be reported here.
** The occupational class must be given if the income earner is covered by occupational accident insurance and receives earnings subject to the occupational accident insurance contribution. Reporting the occupational class is also recommended when the income earner is not covered by occupational accident insurance but is in an employment relationship. Enter the occupational class code according to Statistics Finland’s classification of occupations (TK10). For the classification of occupations, visit the website of Statistics Finland. Contact your insurance provider for instructions for selecting the right code.
*** Earnings-related pension provider code: Select a pension provider and give its code. Examples below:
- 46 Ilmarinen Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 54 Elo Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 55 Varma Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 56 Veritas Pension Insurance Company
**** If you are a temporary employer and submit the report in the Incomes Register’s e-service or on a paper form, you do not need to provide the pension policy number. The number is only required if you submit the report via API or in an upload service.
In addition to the earnings payment report, you must also submit the employer’s separate report on the employer’s health insurance contribution in accordance with Section 4.6.
4.8.4 Paying wages and reimbursement of expenses
When a household pays such compensation as daily allowance, kilometre allowance, or reimbursement of expenses for work equipment, they must also be reported to the Incomes Register.
Example 18: The household pays wages and reimbursement of expenses
The household is a temporary employer and is not registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register. The household pays EUR 2,000 in wages for renovation as a one-off payment, reimbursement of EUR 35 for work equipment, a tax-exempt kilometre allowance of EUR 57 for 100 km for picking up materials, and a partial daily allowance of EUR 24.
The work was performed in April and the wages were paid on 20 April. The household had not paid any other wages during the same year.
The household withholds 25% in taxes from gross wages of EUR 2,000 in accordance with the tax card. No taxes are withheld or social insurance contributions paid from the reimbursement of expenses of EUR 35.
The household also pays a non-wage compensation for work of EUR 150 per month for cleaning to a company that is registered in the prepayment register. The cleaning work is not reported to the Incomes Register at all, as the recipient is registered in the prepayment register.
The household reports the following data to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 20.04.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.04.20xx The end date of the pay period: 30.04.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class*: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code**: NN Pension policy number***: NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay | 2000.00 |
|
331 Daily allowance Type of daily allowance: Partial daily allowance |
24.00 |
|
311 Kilometre allowance (tax-exempt) Number of kilometres: 100**** |
57.00
|
| 353 Taxable reimbursement of expenses | 35.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax | 500.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 173.00 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 30.00 |
* The occupational class must be given if the income earner is covered by occupational accident insurance and receives earnings subject to the occupational accident insurance contribution. Reporting the occupational class is also recommended when the income earner is not covered by occupational accident insurance but is in an employment relationship. Enter the occupational class code according to Statistics Finland’s classification of occupations (TK10). For the classification of occupations, visit the website of Statistics Finland. Contact your insurance provider for instructions for selecting the right code.
** Earnings-related pension provider code: Select a pension provider and give its code. Examples below:
- 46 Ilmarinen Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 54 Elo Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 55 Varma Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 56 Veritas Pension Insurance Company
*** If you are a temporary employer and submit the report in the Incomes Register’s e-service or on a paper form, you do not need to provide the pension policy number. The number is only required if you submit the report via API or in an upload service.
**** The kilometres travelled can be submitted by pay period, but the data must be submitted in the last report of the year at the latest
The household also reports the amount of the employer’s health insurance contribution in the employer’s separate report:
| EMPLOYER'S SEPARATE REPORT | |
|---|---|
| Payer details | |
| Customer identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 | |
| Report details | |
|
Reporting date: 05.05.20xx Payment month: 4/20xx Payment year: 20xx |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 102 Employer's health insurance contribution (total, from EUR 2,000) | 23.20 |
4.8.5 The EUR 1,500 limit is exceeded during the year
When you are paying wages as a household and the EUR 1,500 limit is exceeded during the year, your obligations change. You must withhold tax from the part exceeding the limit and the wages that the income earner may earn during the rest of the year. The employer’s health insurance contribution must be calculated and paid on the basis of the sum for the entire year (including the wages that have already been paid). You can report the whole amount when the limit is exceeded.
Other insurance obligations may also change, see the instructions in Section 4.8.3.
When the income limit is exceeded, you will have to correct the “No obligation to provide insurance” information in previously submitted reports for the insurance policies for which the insurance obligation is changing. Correct each previous report separately.
Make the correction by cancelling, i.e. deleting, the previous report and then submit a completely new report without the inclusion of No obligation to provide insurance. Also enter the details for earnings-related pension insurance in the report, including the pension plan number. If you are a temporary employer, see Section 4.4 for more information on the pension policy number.
Cancel the old report and submit the new report during the same day.
Example 19: The household pays EUR 1,000 in wages (EUR 1,300 has already been paid)
The household is a temporary employer and is not registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register. The household paid the employee EUR 1,300 in wages for renovation work in March. The report was submitted electronically on 5 April. No taxes were withheld or employer’s health insurance contributions paid from the wages, as the wages paid did not exceed EUR 1,500. The wages and other social insurance contributions were duly paid and reported.
In October of the same year, the household pays the same employee EUR 1,000 in wages for another renovation assignment. The wage amount for the full year exceeds the EUR 1,500 limit. According to the employee’s tax card, the withholding rate is 25%. The household must withhold tax from the amount exceeding EUR 1,500 (EUR 800) (EUR 2,300–EUR 1,500). However, the employer’s health insurance contribution is paid and reported for EUR 2,300 (the wage amount for the whole year).
Of the wages paid in October, wages of EUR 1,000 and a withholding of EUR 200 are reported to the Incomes Register. The previous report does not need to be corrected or supplemented.
The household must report the following data on the wages paid in October to the Incomes Register:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 31.10.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.10.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.10.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 Payer's name: Essie Example Payer's address: Example Street 1, 11111 Example |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class*: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code**: NN Pension policy number***: NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay | 1000.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax | 200.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 71.50 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 15.00 |
* The occupational class must be given if the income earner is covered by occupational accident insurance and receives earnings subject to the occupational accident insurance contribution. Reporting the occupational class is also recommended when the income earner is not covered by occupational accident insurance but is in an employment relationship. Enter the occupational class code according to Statistics Finland’s classification of occupations (TK10). For the classification of occupations, visit the website of Statistics Finland. Contact your insurance provider for instructions for selecting the right code.
** Earnings-related pension provider code: Select a pension provider and give its code. Examples below:
- 46 Ilmarinen Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 54 Elo Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 55 Varma Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- 56 Veritas Pension Insurance Company
*** If you are a temporary employer and submit the report in the Incomes Register’s e-service or on a paper form, you do not need to provide the pension policy number. The number is only required if you submit the report via API or in an upload service.
The household also reports the amount of the employer’s health insurance contribution in the employer’s separate report. The month in which the EUR 1,500 limit was exceeded and during which the total amount of health insurance contributions accrued by that time was reported is entered as the payment month.
| EMPLOYER'S SEPARATE REPORT | |
|---|---|
| Payer details | |
| Customer identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 | |
| Report details | |
|
Reporting date: 05.11.20xx Payment month: 10/20xx Payment year: 20xx |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 102 Employer's health insurance contribution (total, from EUR 2,300) | 26.68 |
5 Household and private daycare allowance
If your family hires a babysitter and receives private day care allowance from Kela, Kela acts as the substitute payer of the benefit. Still, the actual employer is the family. In general, the payment of the allowance and the reports go as follows:
- Kela pays the allowance to the babysitter. Before payment, Kela deducts the withholding tax from the allowance and pays it to the Tax Administration.
- Private day care allowance may consist of a care allowance, an income-based care supplement and a municipal supplement. The municipal supplement is paid by Kela or the municipality. In both cases, the payer pays withholding tax on the total amount of the allowance.
- Kela reports to the Incomes Register
- the private day care allowance (can include a possible municipal supplement)
- the withholding tax on the allowance.
- The family must take out insurance for a babysitter in an employment relationship and pay the following social insurance contributions:
- earnings-related pension insurance contribution to the pension provider
- unemployment insurance contribution to the Employment Fund
- accident and occupational disease insurance contribution to an insurance provider.
- With an earnings payment report, the family must submit to the Incomes Register
- the private day care allowance and municipal supplement received by the babysitter as income type Wages paid by substitute payer: the employer pays for the employer's social insurance contributions (321)
- the earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions on the amount of allowance paid by Kela.
- If the family also pays the babysitter other wages in addition to the allowance (see Section 5.2 and Example 21 for more details), the family must use the earnings payment report to also submit to the Incomes Register
- the wages paid by the family in addition to the allowance
- withholding from the wages
- earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions withheld from the wages.
- The family may also have to submit an employer's separate report to the Incomes Register to report the amount of the employer’s health insurance contribution. Read more about the employer’s separate report in Section 4.6.
Make sure that the same family member who made the application on private day care allowance to Kela also takes out the insurance for the babysitter and submits reports to the Incomes Register using their own personal identity code.
Read more in Section 4 of this guideline and in instruction Reporting data to the Incomes Register: payments made by substitute payer, Section 2.3 Private day care allowance (wages).
Of the social insurance contributions, the earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions consist of the employer’s share and the employee’s share. Since the family is an employer, it must collect the employee’s share of the wages paid to the worker and report the amount to the Incomes Register. The family pays both of the social insurance contributions together to the social insurance provider. There is no similar employee’s share in accident and occupational disease insurance contributions.
Read more about social insurance contributions in these instructions in Section 4 Employing an individual to work for a household.
5.1 The family does not pay the babysitter any other pay in addition to the allowance
Even if your family makes no payments to the babysitter, the family must always report the private day care allowance paid by Kela to the Incomes Register. Since the family is the actual employer, it must pay social insurance contributions from the amount of the allowance and report them to the Incomes Register.
As your family makes no payments to the babysitter, you cannot collect the employee’s shares of insurance contributions directly from the babysitter’s wages. You have two options:
- Invoice the employee’s shares from the babysitter. Report the information normally according to example 20 a.
- Pay the contributions on behalf of the babysitter. In this case, the contributions are an employee benefit of monetary value to the babysitter, i.e. a fringe benefit, that must be reported to the Incomes Register. In this case, submit the report in accordance with example 20a, but also report the amount of the contributions with income type Other fringe benefit (317). Note that the contributions are then reported twice: both as a fringe benefit and with income types Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance contribution (413) and Employee’s unemployment insurance contribution (414). The employee’s shares of the contributions are taken into account as a deduction in the babysitter’s taxation. Read more in instruction Reporting data to the Incomes Register: fringe benefits and reimbursements of expenses, Section 1.3 and on reporting in instruction Reporting data to the Incomes Register: payments made by substitute payer, Section 2.3.
Below is a simple example of the report that the family must submit when they invoice the insurance contributions from the babysitter.
Example 20 a: The family receives private day care allowance and does not pay any other wages
The family is a temporary employer, and it has signed a contract with a babysitter from the beginning of May to the end of August. The family receives a private day care allowance from Kela amounting to EUR 470 per month (private day care allowance EUR 170 and municipal supplement EUR 300). Kela pays the allowance directly to the babysitter. A 62-year-old grandparent has been hired as the babysitter. The family pays no other wages to the babysitter.
Kela withholds tax when it pays the private day care allowance to the babysitter and reports that to the Incomes Register. Kela does not collect any social insurance contributions from the sum. The family must invoice the employee’s share of earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions from the babysitter and pay them to the insurance providers together with the employer’s share.
The family must report the allowance paid by Kela as income type 321 and, in addition, the employee’s earnings-related pension insurance and unemployment insurance contributions calculated from it with their respective income types.
The family submits the following report for June:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 30.06.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.06.20xx The end date of the pay period: 30.06.20xx |
|
| Payer details (Actual employer, i.e. the household) | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance)* Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 Payer's name: Essie Example Payer's address: Example Street 1, 11111 Example |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class**: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code: NN Pension policy number: NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 321 Wages paid by substitute payer: the employer pays for the employer's social insurance contributions | 470.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 33.60 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 7.05 |
* If the payer were a contract employer, only Household would be reported as the payer type.
** Enter the occupational class code according to Statistics Finland’s classification of occupations (TK10) here. The occupational classification is available on the Statistics Finland website.
In addition to the earnings payment report, the family must also submit the employer’s separate report on the employer’s health insurance contribution in accordance with Section 4.6, since they know at the start of employment that the EUR 1,500 limit will be exceeded.
Example 20 b: The household pays earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions on behalf of the babysitter because the contributions can no longer be collected under the law
The family has not invoiced the babysitter for the employee’s share of earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions in time, and the contributions can no longer be charged from the babysitter under the law. The family pays the insurer the shares of both the employer and the employee.
The amount of the babysitter’s earnings-related pension insurance contribution is EUR 33.60 and the amount of the unemployment insurance contribution EUR 7.05, which means that the total amount of the insurance contributions is EUR 40.65. The amount paid by the family is not considered to be earnings from work forming the basis for an earnings-related pension, unemployment, or accident and occupational disease insurance contributions.
The family reports the amount it paid to the Incomes Register using income type Other fringe benefit (317) and includes the Insurance information type entry Subject to earnings-related pension insurance contribution: No, Subject to accident insurance and occupational disease insurance contribution: No and Subject to unemployment insurance contribution: No. The income is only subject to a health insurance contribution.
The family must also report the employee contributions it has paid as income types Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance contribution (413) and Employee’s unemployment insurance contribution (414) to have the payment taken into account as a deduction in the babysitter’s taxation.
The information is reported in the earnings payment report of the month when insurance contributions could not be invoiced from the reported wages.
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 321 Wages paid by substitute payer: the employer pays for the employer's social insurance contributions | 470.00 |
|
317 Other fringe benefit Type of insurance information: Subject to earnings-related pension insurance contribution: Basis for insurance contribution: No Type of insurance information: Subject to unemployment insurance contribution: Basis for insurance contribution: No Type of insurance information: Subject to accident and occupational disease insurance contribution: Basis for insurance contribution: No |
40.65 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 33.60 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 7.05 |
Example 20 c: The household voluntarily pays earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions on the babysitter’s behalf
If the family voluntarily pays the earnings-related pension and unemployment insurance contributions on the babysitter’s behalf, even if it still has the legal right to invoice the babysitter for the insurance contributions, this usually constitutes wages subject to social insurance contributions.
The family reports the information to the Incomes Register using the Other fringe benefit (317) income type in the earnings payment reports for the months for which no insurance contributions have been collected. The family must also report the employee contributions it has paid as income types Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance contribution (413) and Employee’s unemployment insurance contribution (414) to have the payment taken into account as a deduction in the babysitter’s taxation.
Since the income is subject to all insurance contributions, the information Type of insurance information is not provided.
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 321 Wages paid by substitute payer: the employer pays for the employer's social insurance contributions | 470.00 |
| 317 Other fringe benefit | 40.65 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution (from EUR 510.65) | 36.50 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution (from EUR 510.65) | 7.66 |
5.2 The family pays the babysitter in addition to the allowance
If the family pays the babysitter other wages in addition to the allowance paid by Kela, the family must
- deduct withholding tax from the other wages and pay it to the Tax Administration (Kela pays the withholding tax on the share of the allowance)
- pay social insurance contributions for the entire amount: both the private day care allowance paid by Kela and the other wages paid by the family.
Since your family pays the babysitter other wages in addition to the allowance, deduct the employee’s shares of the earnings-related pension insurance contribution and the unemployment insurance contribution from the pay before paying it to the babysitter.
If you pay the babysitter other payments on the same date of payment, you can report them with the same report where you report the wages paid by the substitute payer.
This is a simple example of the report that the family must submit in this situation.
Example 21: The household pays wages to a babysitter and receives private day care allowance
The family is a contract employer and has agreed that the babysitter’s wages are EUR 1,000 per month from the beginning of the year. Of this sum, EUR 200 is private day care allowance paid by Kela. The wages paid by the family amount to EUR 800.
The family submits the following report for November:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 30.11.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.11.20xx The end date of the pay period: 30.11.20xx |
|
| Payer details (Actual employer, i.e. the household) | |
|
Payer type: Household Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 Payer's name: Essie Example Payer's address: Example Street 1, 11111 Example |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class*: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code: NN Pension policy number: NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay | 800.00 |
| 321 Wages paid by substitute payer: the employer pays for the employer's social insurance contributions | 200.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax (from EUR 800) | 220.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution (from EUR 1,000) | 71.50 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution (from EUR 1,000) | 15.00 |
* The occupational class according to Statistics Finland’s classification of occupations (TK10) must be specified because the income earner is covered by occupational accident insurance and receives earnings subject to the occupational accident insurance contribution. Your insurance provider will provide you with the correct occupational class. You can also find the codes on the Statistics Finland page on the classification of occupations.
If the payer were a temporary employer, payer type Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) would be given as the second payer type.
In addition to the earnings payment report, the family must also submit the employer’s separate report on the employer’s health insurance contribution in accordance with Section 4.6.
Here is an example of a report that a family must submit when the babysitter is paid less than EUR 1,500 per year and receives private day care allowance:
Example 22: A household pays a babysitter wages totalling less than EUR 1,500 per year and receives private day care allowance
The family is a temporary employer and has agreed that the 52-year-old babysitter’s wage for June is €1,400, of which €200 is private day care allowance paid by Kela. The wages paid by the family amount to €1,200.
The employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution must always be collected from the employee, even if the employer has no payment obligation because the €1,500 limit applied to the employer is not exceeded. As less than €1,500 per year is paid in wages, the wages are not subject to the health insurance contribution or the accident and occupational disease insurance contribution. For this reason, the household enters No obligation to take out insurance for these two contributions.
Because the household does not need to pay the employer’s health insurance contribution, the employer’s separate report is not required either.
The family submits the following report for June:
| REPORT DETAILS | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 30.06.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.06.20xx The end date of the pay period: 30.06.20xx |
|
| Payer details (Actual employer, i.e. the household) | |
|
Payer type: Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 Payer's name: Essie Example Payer's address: Example Street 1, 11111 Example |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Type of exception to insurance: Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code: *NN Pension policy number: **NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay | 1200.00 |
| 322 Wages paid by substitute payer: employer pays for employer’s earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 200.00 |
| 323 Wages paid by substitute payer: employer pays for employer’s unemployment insurance contribution | 200.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax (from EUR 1200) | 252.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution (from EUR 1,400) | 100.10 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution (from EUR 1,400) | 21.00 |
* Earnings-related pension provider code: Select a pension provider and give its code.
** If you are a temporary employer and submit the report in the Incomes Register’s e-service or on a paper form, you do not need to provide the pension policy number. The number is only required if you submit the report via API or in an upload service.
Collecting contributions from wages is not always possible. This is the case in the following situations:
- The amount of the other wages is not sufficient to cover the employee’s share of insurance contributions. In this situation, if you pay the contributions on the babysitter’s behalf, they will still constitute a fringe benefit for the babysitter. Report the employee’s contributions as a fringe benefit under income type Other fringe benefit 317 and, in addition, report the same sums as collected employee contributions under income types 413 and 414.
- In certain situations, it is no longer possible to collect insurance contributions from the babysitter’s wages, for example if wages are no longer paid or if the legal deadline for adjusting social insurance contributions has been exceeded. In such a situation, if you pay the contributions on the babysitter’s behalf, the income will exceptionally only be subject to the health insurance contribution. In this case, report the contributions using income type Other fringe benefit (317) and, in the report, include the Insurance information type as Subject to earnings-related pension insurance contribution: No, Subject to accident insurance and occupational disease insurance contribution: No and Subject to unemployment insurance contribution: No. In addition, report the same sums as collected employee contributions under income types 413 and 414. For more information on adjusting an employee’s social insurance contributions, see instruction Correcting data in the Incomes Register, Section 3.3.
For information on the pay of an au pair, see the Tax Administration’s instruction Au pairs from abroad arriving in Finland and instruction Reporting data to the Incomes Register: international situations, Section 3.6.
6 Pool of household employers
Households can jointly pay wages to a single income earner for such work as cleaning. In that case, they form a pool of household employers.
When the members of the pool hire an employee under one common employment contract, they are jointly responsible employers of the employee. In that case, the members of the pool of household employers are jointly responsible for managing the employer obligations related to the employment relationship.
The households must agree among themselves who will represent the pool in contacts with parties outside the pool. The representative
- withholds tax from the wages and pays the withholding tax
- calculates the employer’s health insurance contribution and pays it
- manages all other employer obligations (takes out the earnings-related pension insurance, accident and occupational disease insurance, and pays unemployment insurance contributions.
The representative must use their personal identity code when submitting reports and making payments. When you report wages on behalf of the pool, you must enter Household and Pool of household employers as payer types.
The euro limits for taking out insurance and other employer obligations are described in Section 4.1. Remember also the following when reporting information on behalf of the pool of household employers.
- Earnings-related pension insurance and accident and occupational disease insurance: If the pool representative takes out the insurance policies on behalf of the pool, the annual limits specified in the policies apply to all pool members. If each of the households has taken out its own insurance, the limits apply to each household separately.
- Unemployment insurance: The EUR 1,500 limit applies to the entire pool. This means that the Employment Fund will only impose the contribution when the pool has paid more than EUR 1,500 in wages per year to the employee/employees. However, the employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution must also be collected from smaller wages paid to the employee.
- Withholding tax and employer’s health insurance contribution: The EUR 1,500 limit applies to each member of the pool separately, and the total amount paid by the pool or a family is irrelevant.
- If each household concludes a separate employment contract with the employee, each of them has a separate employment relationship with the employee, and the arrangement is not considered a pool of employers.
The pool must observe the general age limits for insurance policies. For information on the age limits, see Section 4.1.
See Section 3 for instructions for situations where the pool of household employers pays the income earner a non-wage compensation for work instead of wages. No information needs to be reported to the Incomes Register if the income earner is registered in the prepayment register. If the income earner is not registered in the prepayment register, you must withhold tax from the non-wage compensation for work. Only the amounts of payment and withholding are reported as income data to the Incomes Register. Other social insurance contributions are not paid or reported.
If the pool of household employers has a business ID that it uses to pay wages or non-wage compensation for work, the lighter obligations concerning household employers are not applied to the pool (such as the EUR 1,500 withholding limit or the deadline for reporting information to the Incomes Register). In that case, the pool of household employers reports the data to the Incomes Register in the same way as other employers. Visit the website on reporting earnings payment data or see instructions Wages: reporting data to the Incomes Register for more information.
Section 2.3 of the Instructions on substitute payers includes an example of a report submitted as a pool of households.
7 Correcting data reported to the incomes register
If there is an error in the data reported to the Incomes Register, the data must be corrected.
Read more in Correcting data or in instructions Correcting data in the Incomes Register.
7.1 Replacement report
If you want to change a report that you have already submitted, you must correct the information by submitting a replacement earnings payment report.
If you have reported earnings payment data for several employees, you only need to submit a replacement report on the employee whose earnings payment data needs to be corrected. In certain situations, data must be corrected by cancelling the previously submitted report and by giving a new report. Read more about cancelling a report in Section 7.2.
If you have paid and reported the employer’s health insurance contribution and the correction affects its total amount, you must also submit a replacement employer’s separate report.
In the replacement report, you must always give the changed information and the information that was correct in the original report. The replacement report will replace the original report in its entirety. The latest report saved in the Incomes Register is always the valid report.
If you correct information in an individual report in the Incomes Register’s e-service, you can open the original report and only correct the incorrect information. The other data will remain the same. If you send the corrections on a paper form, make sure to enter all information again in the report.
For example, if you have paid EUR 800 in wages and accidentally reported the wages as EUR 80 in the original report, report all the previously reported data as such in the replacement report and the corrected earnings payment data as EUR 800.
The correction is targeted at the original report using the report reference. When you submit a new report to the Incomes Register, two references are attached to the report in the Incomes Register.
- Payer’s report reference: You can generate the reference yourself or leave the field blank, in which case the Incomes Register generates the reference automatically. If you prepare the report in the Incomes Register’s e-service, you will see the reference on the confirmation page after sending the report. If you submit the report on a paper form and leave the reference blank, the Incomes Register will send you the automatically generated reference as a letter.
- Incomes Register report reference: A technical system reference is also generated for each report and this reference can also be used to target the correction. However, the system reference is long and complex and for this reason, it is usually better to use the payer’s own report reference.
If you do not use the reference of the original report in the replacement report, the report will not replace the previous report; instead, it will be saved in the Incomes Register as a new report. In that case, the incorrect income data is saved twice in the Incomes Register.
You should correct the incorrect report as soon as you notice the error. There is no specific deadline for this. All incorrect data must be corrected, whether it is mandatory data or voluntarily submitted supplementary data. If a mandatory data item was missing from the original report, it must also be added to the replacement report.
If you submitted the report in the Palkka.fi service, you can also correct the report there.
If you correct social insurance contribution amounts, employment-pension and insurance providers will get the corrected information from the Incomes Register and correct their invoicing accordingly.
Example 23: The household corrects the amount of the wages on a replacement report
The household pays EUR 40 to an individual aged 15 as a one-off payment in the same manner as in Example 12.
The household accidentally reports EUR 60 as the amount of wages to the Incomes Register:
| FIRST REPORT BEFORE THE ERROR IS DETECTED | |
|---|---|
|
Type of action: New report Payer's report reference: 20xx0120 |
|
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 20.01.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.01.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.01.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (earnings-related pension, health, unemployment or accident and occupational disease insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay* | 60.00 |
When the household notices the error, it submits a replacement report to the Incomes Register. It contains the same information as the first report, but the euro amount has been corrected:
| REPLACEMENT REPORT | |
|---|---|
|
Type of action: Replacement report Payer's report reference:20xx0120 |
|
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 20.01.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.01.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.01.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (earnings-related pension, health, unemployment or accident and occupational disease insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay | 40.00 |
If the household corrects the information in the Incomes Register’s e-service, it can open the original report and only correct the incorrect information. If you use a paper form, you must complete the whole report again and add the report reference of the original report to the corrected report.
7.2 Correction by cancellation
Although information in the Incomes Register is usually corrected with a replacement report, in certain situations the earlier report must first be cancelled (deleted from the Incomes Register), and an entirely new report must then be submitted.
Correct an earnings payment report by cancelling it only if there are errors in the following information or information must be changed:
- payment date
- pay period
- the payer’s or income earner’s customer identifier (e.g. personal identity code or business ID)
- the income earner’s date of birth
- type of additional income earner data: athlete or corporate entity
- payer type: temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy)
- pension policy number
- occupational accident insurance provider identifier or insurance policy number
- type of exception to insurance
- ‘No obligation to take out insurance’ data
- ‘Not subject to Finnish social security’ data
- ‘Voluntary insurance in Finland (earnings-related pension insurance)’ data
Cancel the old report and submit the new report during the same day.
Correct an employer’s separate report by cancelling it only if the error involves some of the data types below or the data must be changed:
- reporting period
- payer’s customer identifier (personal identity code)
- pension policy number
- occupational accident insurance provider identifier or policy number.
Data is cancelled differently in different reporting channels. If you cancel an individual report in the Incomes Register’s e-service, retrieve the previously submitted report to be cancelled and select ‘Cancel’. If you cancel the report on a paper form, use the same form as when submitting a new report but select ‘Report cancellation’ as the type of action.
Example 24: The household corrects ‘No obligation to take out insurance’ entry by cancellation
The household is a temporary employer and is not registered in the Finnish Tax Administration’s employer register. The household pays EUR 1,000 to a contractor for building a partition wall.
The payment is subject to the earnings-related pension insurance contribution but not to the health insurance or accident and occupational disease insurance contributions. Even if the EUR 1,500 limit for unemployment insurance is not exceeded, the household must collect the employee’s share of the unemployment insurance contribution from the wages. In that case, the employer ends up with the unemployment insurance contribution.
The household reports the data to the Incomes Register as follows:
| FIRST REPORT | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 15.06.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.06.20xx The end date of the pay period: 15.06.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code: NN Pension policy number: NNNNNNN Type of exception to insurance: No obligation to provide insurance (accident and occupational disease insurance) No obligation to provide insurance (health insurance) |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay | 1000.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 71.50 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 15.00 |
Later during the same year, it became necessary to hire the renovation contractor again. It was agreed that the contractor would be paid EUR 600 for the work. With the new payment, the wages paid during the year exceed EUR 1,500, which is the limit for taking out unemployment insurance, accident and occupational disease insurance, employer’s health insurance, and tax withholding.
For this reason, the previous report must be corrected and the entries ‘No obligation to take out insurance (accident and occupational disease insurance)’ and ‘No obligation to take out insurance (health insurance)’ must be deleted from the report. ‘No obligation to take out insurance’ entry cannot be corrected with a replacement report.
The household must also withhold tax from the amount exceeding EUR 1,500 (EUR 1,600 – EUR 1,500 = EUR 100) in accordance with the tax rate entered on the tax card (10%). The employer’s health insurance contribution is paid and reported for EUR 1,600, i.e. the wage amount for the full year.
Thus, the household has to first cancel the previous report and then submit a new report with the correct data. To do so, the household logs in to the Incomes Register’s e-service, locates the previous report using the report search function and clicks ‘Cancel’. After the previous report is cancelled, the household submits a new report with the correct data. The new report must be submitted immediately after the cancellation of the previous report.
| NEW REPORT SUBMITTED AFTER THE CANCELLATION | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 15.06.20xx The start date of the pay period: 01.06.20xx The end date of the pay period: 15.06.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code: NN Pension policy number: NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay | 1000.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 71.50 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 15.00 |
When the household later makes the additional payment of EUR 600, it submits a separate report for the payment date in question.
| REPORT SUBMITTED FOR A LATER PAYMENT | |
|---|---|
| Type of action: New report | |
| Pay period | |
|
Payment date: 20.08.20xx The start date of the pay period: 16.08.20xx The end date of the pay period: 31.08.20xx |
|
| Payer details | |
|
Payer type: Household Payer type: Temporary employer (no TyEL insurance policy) Name of the contact person: Essie Example Contact person's telephone number: 0000000 Contact person’s email: example@example.fi Payer's identifier (personal identity code): 010101-1111 |
|
| Income earner details | |
|
Income earner's identifier (personal identity code): 020202-2222 Occupational class: 12345 Earnings-related pension insurance data: Employee’s earnings-related pension insurance Earnings-related pension provider code: NN Pension policy number: NNNNNNN |
|
| INCOME TYPE DETAILS | EUR |
| 201 Time-rate pay or 227 Contract pay | 600.00 |
| 402 Withholding tax | 6.00 |
| 413 Employee's earnings-related pension insurance contribution | 35.75 |
| 414 Employee's unemployment insurance contribution | 7.50 |
Read more in Correcting data in the Incomes Register.
8 Mandatory data and deadlines in the table
| Payer | Mandatory data in the report | Deadline for electronic report | Deadline for paper form |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A casual employer
|
|
Fifth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
Eighth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
|
A casual employer
|
|
Fifth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
Eighth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
|
A regular employer
|
|
Fifth calendar day after the payment date |
Eighth calendar day after the payment date |
|
A regular employer
|
|
Fifth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
Eighth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
|
A regular employer
|
|
Fifth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
Eighth day of the calendar month following the payment month |
|
A regular employer
|
|
No wages payable: fifth day of the next calendar month |
No wages payable: eighth day of the next calendar month |
|
All payers Complementary data
|
For example:
|
No deadline. We recommend that you report the supplementary information together with mandatory data. |
No deadline. We recommend that you report the supplementary information together with mandatory data. |
|
All payers Data submitted on a replacement report
|
|
No deadline. Must be corrected immediately after the error has been detected. |
No deadline. Must be corrected immediately after the error has been detected. |
|
All payers Data to be submitted when cancelling a report
|
|
No deadline. Must be cancelled immediately after the error has been detected. |
No deadline. Must be cancelled immediately after the error has been detected. |
